Electricity Free Cooling System
Pottery making is truly originated in African tradition. In northern Nigeria, earthenware pots have been used since past as cooking food as well as water storage containers, coffins, wardrobes and banks. At present, these particular clay pots are roughly extinct, substituted by aluminum containers even more modern techniques of burying the dead, keeping clothes and saving money.
Born in 1964 into a family of pot makers and raised in the rural north, Mohammed Bah Abba was familiar from an early age with the various practical and symbolic uses of traditional clay pots, and learned as a child the rudiments of pottery. Subsequently studying biology, chemistry and geology at school, he unravelled the technical puzzle that led him years later to develop the "pot-in-pot preservation/cooling system".
He was selected as a Rolex Laureate in 2000 for this ingenious technique that requires no external energy supply to preserve fruit, vegetables and other perishables in hot, arid climates. The pot-in-pot cooling system, a kind of "desert refrigerator", helps subsistence farmers by reducing food spoilage and waste and thus increasing their income and limiting the health hazards of decaying foods. Abba says he developed the pot-in-pot "to help the rural poor in a cost-effective, participatory and sustainable way".
The pot-in-pot consists of two earthenware pots of different diameters, one placed inside the other. The space between the two pots is filled with wet sand that is kept constantly moist, thereby keeping both pots damp. Fruit, vegetables and other items such as soft drinks are put in the smaller inner pot, which is covered with a damp cloth. The phenomenon that occurs is based on a simple principle of physics: the water contained in the sand between the two pots evaporates towards the outer surface of the larger pot where the drier outside air is circulating. By virtue of the laws of thermodynamics, the evaporation process automatically causes a drop in temperature of several degrees, cooling the inner container, destroying harmful micro-organisms and preserving the perishable foods inside.
Universal Technique
The principle of physics used by the pot-in-pot is present in nature itself. A panting dog, for example, uses the same process, losing heat through its tongue. It is also well known by humans in arid countries. Indeed, the roots of innovation spread wide and deep, and Abba’s pot-in-pot is one of several ingenious applications of cooling by evaporation.
The city of Qena in Upper Egypt is renowned for its porous-clay cooling vessels — a tradition spanning more than three millennia. In Burkina Faso, the Jula people’s traditional jars are sometimes soaked in water before goods are stored in them, so that they stay cool by evaporation. This single-pot design is similar to the pot-in-pot, but less efficient.
In India, street vendors often cool fruit or drinks for their customers by suspending bags of produce in a porous clay container. Also in India, a rectangular enclosure of wet bricks is used to preserve foodstuffs from heat. Water seeps slowly through the porous bricks, evaporating from the surface and keeping the entire structure cool. The Punjab Agricultural University in Ludhiana has recently tested an improved version of this system, which is closer to the pot-in-pot than any other device. It uses double-brick walls, with wet sand between them. The sand is kept wet, and the entire chamber is covered with a moist mat. Fruit and vegetables inside the chamber are maintained at temperatures below 20° C.
In 1992, laboratory experiments to measure the temperature drop in a two-pot design, where a small clay receptacle is placed within another receptacle filled with water, were carried out at the University of Benin City by Nigerian professor Victor Aimiuwu. He found that the device had good cooling properties, remaining up to 14 degrees cooler than the surrounding environment.
Theory into Practice
Still, among all the similar devices and traditional cooling pots, there is nothing quite like the pot-in-pot with its unique combination of simplicity and effectiveness. In fact, the Nigerian teacher’s project shows how, for the Rolex Awards, originality is far more than a bright idea — it means turning an inspiration into a concrete achievement with a major impact.
"Mohammed Bah Abba won a Rolex Award not simply because he designed the pot-in-pot. He overcame obstacles to produce and distribute it, and also ensured that it could be bought for an affordable price by the people who need it," says Rebecca Irvin, head of the Rolex Awards Secretariat in Geneva.
To understand the relevance of Abba’s Rolex Award-winning project, it is necessary to look at the geography of northern Nigeria and the restricted lives led by the people. This region is primarily a semi-desert scrubland inhabited by a large, mostly agriculture-based population, the majority of who live in abject poverty. Polygamy is a dominant feature of the family structure and women living in purdah are confined to their homes and seriously disadvantaged in terms of health care, education and employment opportunities. Young girls are particularly enslaved because they are forced to go out each day and rapidly sell food that would otherwise perish, in order to add to the meager family income.
A key reason for the pot-in-pot’s success is the lack of electricity in most of the northern rural communities, for without electricity there can be no refrigeration. Even in towns and cities the power supply is erratic. Most of the urban poor cannot even afford refrigerators.
Personal Inspiration
In a developing nation facing severe communication, transport and utility problems, Abba set out to try and help improve the ailing economy. He became a lecturer in business studies at Jigawa State Polytechnic in Dutse in 1990. When not teaching, Abba serves as a consultant to the regional United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Jigawa, organising community activities and giving seminars. A staunch supporter of women’s rights, he is also a consultant with the state’s Ministry for Women Affairs and Social Mobilization.
These consultancies brought Abba in close contact with rural communities, where he observed the extreme hardships suffered by subsistence farmers and their families. "Through these observations, I became motivated to revitalise earthen pot usage and extend the life of perishable foods," he explains.
Abba’s first trials of the pot-in-pot proved successful. Eggplants, for example, stayed fresh for 27 days instead of three, and tomatoes and peppers lasted for three weeks or more. African spinach, which usually spoils after a day, remained edible after 12 days in the pot-in-pot.
The enterprising teacher persistently refined his invention for two years between 1995 and 1997. He then tapped into the large unemployed local workforce and hired skilled pot makers to mass produce the first batch of 5,000 pot-in-pots. Manufacturing these devices at his own expense, he began distributing them for free to five villages in Jigawa. For this initial phase of his project, he received limited financial backing from his brother and assistance in the form of transportation, fuel and labour from the UNDP, the regional government, a local women’s development group and the Jigawa State Polytechnic.
In 1999, Abba supplied another dozen local villages with 7,000 pots, again at his expense. Sold for between US$2 for the smaller pot-in-pots and US$4 for the bigger version, the pot-in-pot stays affordable, while the proceeds from sales help finance manufacturing and distribution costs.
Lesson for Villagers
However, one of the biggest obstacles faced by the project was educating the villagers about this simple technology. Abba devised an educational campaign tailored to village life and the illiterate population, featuring a video-recorded play by local actors who dramatise the benefits of the desert refrigerator. Abba began showing the video in villages using a makeshift cloth screen and a portable projector and generator. "Nightfall is best," he comments, "because this is when farmers head home and are keen to watch an entertaining presentation."
Thanks to a "very timely" Rolex Award, Abba has been able to distribute pot-in-pots in 11 northern Nigerian states, and further his expansion plans in other countries such as Cameroon, Niger, Chad and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
In 2002, with Abba’s approval, the Intermediate Technology Development Group (ITDG) and the University of Al Fashir carried out experiments in Sudan to assess the performances of the pot-in-pot in food conservation. The excellent results led the Women’s Association for Earthenware Manufacturing in Darfur to manufacture their own pot-in-pots, called zeer in Arabic.
As of early 2005, Abba had distributed a total of 91,795 pot-in-pots. "My life has greatly changed since receiving the Rolex Award," he says.
And the future is bright. The Nigerian Laureate has been asked to help introduce and adapt his cooling device in Eritrea, where it could preserve insulin vials for diabetic patients in remote rural areas, as well as in India, Haiti and Honduras.
Transforming Rural Life
The impact of the pot-in-pot on individuals’ lives is overwhelming. "Farmers are now able to sell on demand rather than ‘rush sell’ because of spoilage," says Abba, "and income levels have noticeably risen. Married women also have an important stake in the process, as they can sell food from their homes and overcome their age-old dependency on their husbands as the sole providers." In turn and, perhaps most significantly for the advancement of the female population, Abba’s invention liberates girls from having to hawk food each day. Instead, they are now free to attend school and the number of girls enrolling in village primary schools is rising.
These factors, coupled with the effect that the pot-in-pot has had in stemming disease, are, in Abba’s words, making "the pot-in-pot a tangible and exciting solution to a severe local problem".
Well known for his dedication, Abba is also praised for his concern with the social and economic development of his fellow Nigerians. "Mr Abba cares for the progress of society in general," says Mrs Hadiza Abdulwahab, president of the local Society for Women Empowerment and Development.
The permanent secretary of the State Ministry of Women Affairs and Social Mobilization, Mrs Rabi Umar, agrees. She believes that Abba has been "selfless and tireless" in his efforts to make his project succeed. Summing up his work, she says: "The pot-in-pot project is the first to use simple cultural solutions to address the primary needs of the rural northern Nigerian population, for whom the basic necessities of life are nearly non-existent."
Via: rolexawards.com
Google Project Loon: Wi-Fi for rural areas via Ballons
Google has launched 30 experiment balloons in New Zealand to analyze the circumstance of delivering internet connection via balloon. Some individuals remember this in the year 2008 this idea was talked under the auspices that Google may possibly float several balloons to provide mobile services in rural places. The idea is not relatively new, organizations provide this kind of connectivity via balloons that have been for several years. The services up to now have been rather limited however.
Project Loon in fact has likely to be much more significant to Google in the short-term compared with other initiatives similar to Google Fiber and Glass. Considering that Google is an advertising company, having a lot of people online provides a direct advantage to Google’s bottom line. The project will involve launching balloons which will float in the stratosphere, nearly 10-20 kilometers above. The preliminary evaluation has been undertaken in the Canterbury and Christchurch areas of New Zealand. The balloons are operated by solar panels, and the equipment is hung beneath the inflated balloon.
Every balloon may be able to supply coverage that spans a ground area of around 40 kilometers in diameter supplying speeds around to what 3G delivering now. The radio bands utilized in the experiment are in the unlicensed spectrum of 2 .4GHz and 5 .8GHz. The benefits over satellite connectivity are noticeable , dealing with balloons is quite a bit cheaper compared to launching a rocket. The technical challenges which will be analyzed will of course be relevant to performance, latency, and how easy the evidence of an idea does work to handle the balloons. The final thing everyone wants to take place is to observe one of these things descend into the flight pathways of commercial air traffic.
One thing that is apparently a variable is the speed. Google assures the wind speed in the stratosphere is slow, therefore making balloon survivability achievable. However, a person with any relation to aviation is aware that winds-aloft tend to be quite high, as in hundreds of miles per hour.
But still, Google’s idea does take on and since the idea has already been utilized through other applications, Google’s decide to bring it a step further will likely be remarkable to watch take to the air.
Self-driven Cars are on the Way
The driver-less automobiles are usually considered only an imagination. But, they might be present at roads close to you much earlier than you possibly think about, thanks to an inspiring future of driver-less automobile industry in the horizon. Mercedes is presently developing a model of its own S-Class that is capable of operating without driver provide at speeds of nearly 25 mph. The company guarantees that this is going to be introduced before the end of 2013. The automobile utilizes ultrasonic sensors and also long distance radar devices to guide the road as well as detect possible roadblocks for instance other road users or pedestrians. The significant benefit from this will absolutely be the capability to reduce annoying inner city driving or simply when you find yourself being stuck in a traffic jam.
Mercedes, General Motors as well as Audi has actually slipped under the radar when compared to Google’s driver-less equipment which has not just gotten the headlines, but as well asked a variety of states in the USA to switch their legislation with regard to the usage of driver-less automobiles.
Up to now, Google’s customized Toyota Prius has accomplished over 140, 000 miles of testing 100 percent flawlessly. The only incident the vehicle has become involved in was when it was rear ended by another motorist while still at traffic lights. Google is presently guessing that they will be having the equipment accessible to the public between 2016 and 2018. But, there are a number of concerns yet to be clarified regarding the future of autonomous automobiles. Another thing that is for sure is that Google will not appear to be going to establish their particular car brand. There is absolutely no sign of manufacturing facilities and no designs that have been posted, which might give the company an activity when they were planning to strike the 2016-2018 deadlines.
Self-driven automobiles are thereby impossible to come to be the mainstream within the following decade; however they are much closer to becoming a reality for early adopters than is generally realized.
A Russian Billionaire wants to become Immortal
A 32-year-old Russian billionaire Dmitry Itskov hopes to live permanently and media mogul believes he is able to do this by creating an android body system by the year 2045. There are some weak points to Itskov’s idea, however that hasn’t ended around 20, 000 individuals from publicly supporting the site outlining his program of utilizing android bodies for immortality. Dubbed the 2045 Initiative, Itskov is promoting his idea as the "next step" in human evolution, or "neo-humanity," as he refers to it.
It doesn't keep with android bodies, either. The 2045 people are also asking for a new religion and also group of ethics for the reason that they don’t believe some of the present ones can manage the societal effects of living forever—as many of the present ones have you dying first to be able to attain immortality . Itskov also has progressed forward and endorsed his own political party in Russia known as “Evolution 2045.”
His future , that “new period of controlled evolution ,” goes something like this : By 2020 , Initiative 2045 targets to create this avatar technology available and mainstream—never mind that’s seven years from these days and a running prototype doesn’t exist yet . By 2025, Itskov predicts an “autonomous life-support system for the human brain linked to a robot." Quite simply, they'll have the technology for implanting the human brain into the robot. By 2035, a human should be capable to upload their brain into a robot, and by 2045 our bodies might be changed to holograms. When this occurs, Itskov states we will become "a new species.”
Apart from developing the technology required for this type of evolution, Initiative 2045 has a number of “key” future projects beyond attempting to start an “international social movement." Along with a social network known as immortal.me , Itskov lists the projects he desires to begin : a a non-profit foundation known as Global Future 2045 , the “scientific research centre ‘Immortality ,’” “a business incubator” without more elaboration , a “University of ‘Immortality ,’” and an “annual award for contribution to the realization of the project of ‘Immortality .’”
To encourage appreciate these goals is the Global Future Congress, which conducted its very first meeting in Moscow a year ago. The congress is going to meet again in New York City this June, in which guarantees to introduce the most human-like robot the World has ever seen.
Some practical advantages of Itskov’s type of technology are for the application of medical purposes in designing an alternative body. Itskov says also that this kind of avatar technology also permits you “work in harmful environments” or even “perform rescue operations.”
Via: motherboard.vice.com
3D Laser Scanning Technology: Structural Mapping for Buildings
A new laser scanning technology created by Scott Page Design, the security of your home will never be the same. The technology allows depth mapping even within those walls of yours. The powerful laser has the capacity to scan both the exterior and even the inner surface of. The laser scanning technology’s main application is to document as well as to show architectural flaws and transformations previously unimaginable. With this particular technology, we can easily map the entire world in outstanding detail, that is certainly something that before was nearly impossible without spending hundreds of thousands of years onto it.
Consider 3D laser scanning for:
- As-Built Deliverables: plans, sections and elevations
- 3D modeling
- Heritage surveys
- Site planning
- Animated fly-throughs
- MEP and Electrical layouts
- Reverse Engineering
- Clash Detection
Accuracy
Accurate measurements have always been a crucial element in the design process, from initial design studies through final construction documents. This is especially true for as-built conditions that require a thorough building survey before design work commences. In the past, measurements were typically taken with a tape measure, paper and pencil. The structure was pieced together from countless dimensions, photos, and experience. As the project evolved, frequent site visits were often necessary to fill out gaps in the information. With diligence, a typical drawing set would be accurate enough to guide the project through the planning department to the builder, who was left to sort out remaining irregularities. 3D laser scanning provides a better way to quickly and accurately capture as-built conditions for building documentation.
3D imaging is a relatively new development for architects, though it has been a valuable tool for engineers, surveyors and cartographers for the past decade. As scanner prices have declined and CAD software packages evolved to accept scan data, 3D laser scanners have finally reached architects and design professionals, improving dimensional accuracy and hastening as-built documentation, leaving more time for creativity and innovation.
Advantages
- Almost any project that requires accurate as-built information can benefit from 3D imaging: Measurement accuracy of ±2mm (depending on distance to measured object).
- Unobtrusive data capture methods.
- Reduced costly ‘return’ site visits.
- Rapid data capture of large volumes with increased accuracy.
- Measurements can be made quickly and easily when required without the need for return site visits.
- Shorter project times with a rapid turnaround of information.
- Point clouds can be checked and measured using free viewing software, from any scan location.
- Digital records.
Laser Scanning Applications
- Architectural design
- Heritage surveys
- Structural engineering
- Deformation analysis
- Clash detection
- Manufacturing
- Commercial real estate
- Insurance documentation
- Documenting construction progress
Via: scottpagedesign.com
German Wi-Fi Network Breaks Speed Record 40Gbit per second
Experts of the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics along with the Karlsruhe Institute for Technology have accomplished the wireless transmission of 40 Gbit/s at 240 GHz over a certain distance of one kilometer. Their newest presentation puts a new world record and even links in seamlessly with the potential of optical fiber transmission. In the near future, like radio links has the ability to close gaps in delivering internet by supplementing the network in remote areas and also spots that are not easy to access.
Electronic, mobile phone as well as networked – transforming media consumption habits of modern society demand the much faster transmission of increasing volumes of data. In comparison with the European standard, Germany lags behind in the increase in the fiber-optic network , based on research from the FTTH Council Europe. Deploying modern fiber-optic cables is expensive and even complicated whenever there are natural or urban barriers for instance rivers or perhaps traffic junctions. Broadband radio links help get over this kind of crucial places, in this manner empowering the development of the network infrastructures. In rural areas they are generally an inexpensive as well as a very useful substitute for “Fiber to the Home”.
Experts have finally established a new world record in wireless data transmission: For the very first time, completely integrated electronic transmitters with receivers have been made for a frequency of 240 GHz, that enables the transmission of data rates of up to 40 Gbit/s. This is equivalent to the transmission of an entire Dvd movie in under a second or simply 2400 DSL16000 internet connections. Ranges of over one kilometer are actually covered by utilizing a long range demonstrator, which the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology establish between two skyscrapers as part of the project “Millilink”. “We have managed to develop a radio link based on active electronic circuits, which enables similarly high data rates as in fiber- optic systems, therefore allowing seamless integration of the radio link”, states Prof. Ingmar Kallfass, who coordinated the project at Fraunhofer IAF within the field of a Shared Professorship between IAF and KIT. As 2013, Kallfass with the University of Stuttgart, whereby he continues to take the project.
High Frequencies allow Fast Data Transmission
Utilizing the high frequency range between 200 and 280 GHz not only allows the quick transmission of large volumes of data, but will also bring about compact technical assembly. As the size of electronic circuits and also the antennae scales with frequency/ wavelength, the transmitter and receiver chip only measures 4 x 1.5 mm². The semi-conductor technology designed at Fraunhofer IAF, based upon transistors with high carrier mobility ( HEMT ), makes it possible to employ the frequency between 200 and 280 GHz with active transmitters and receivers in the form of compact, integrated circuits. The atmosphere displays low attenuation with this frequency range, which allows broadband directional radio links. “This makes our radio link easier to install compared to free-space optical systems for data transmission. It also shows better robustness in poor weather conditions such as fog or rain”, states Jochen Antes of KIT.
Up to this time, radio links were unable to directly transfer the data rates of glass fiber. It might change in the future, since the test setup of the project exhibits. Like an excellent performance system would even have the advantage of the so-called bit transparency, i.e. ( the signal of a glass fiber could be fed directly and also without energy-consuming transcoding into a radio link). This could then be transmitted and redirected into a glass fiber. The record data from the test setup is usually the initial stages. “Improving the spectral efficiency by using more complex modulation formats or a combination of several channels, i.e. ( multiplexing, will help to achieve even higher data rates”, states Antes. This might provide groundbreaking momentum to the development of the broadband network.
Via: kit.edu
A Urine Fueled Generator
There are four African young ladies have made a generator that produces electricity for six hours utilizing one liter of urine as fuel. There generator was unveiled at last week's Maker Faire in Lagos, Nigeria, by the four highschool students Akindele Abiola, Duro-Aina Adebola and Faleke Oluwatoyin, all age 14, and Bello Eniola, 15.
Images: makerfaireafrica.com
There urine-powered generator exactly works:
- The gas cylinder pushes hydrogen into a cylinder of liquid borax, which is used to remove the moisture from the hydrogen gas.
- The hydrogen goes into a water filter for purification, which then gets pushed into the gas cylinder.
- Urine is put into an electrolytic cell, which separates out the hydrogen.
- This purified hydrogen gas is pushed into the generator.
As the Next Web portrays it, the Maker Faire is planned to highlight creations "that solve immediate challenges and issues, and afterward works to support and propagate them. Put an additional way, this isn't only a bunch of rich individuals discussing how their applications are set to change the planet."
via: news.yahoo.com
How Strong and Secure is Your Password?
A password is generally a secret word along with series special characters and numbers that’s used in authentication, to help you to prove identification along with gain access to some sort of account. An appropriate password needs to be managed secret from those prohibited to gain accessibility. There’s not necessarily for an account password to be precise words or numbers, an account password which is definitely not precise words or numbers, moreover combining with special characters can be more difficult for someone to guess a desirable protected account. But during this day there are advance software’s have been developed by some bad guys to generate a particular correct combination of a password within just a minute.
That’s why it’s better to update and to know how secure and strong your account password is. Then I recommend some kind of “Password Checker”. Lately, when I search the phrase “Password Checker” on the Google Search Engine I came up with some results. Based on the results, I found three websites which offer a free service in checking a password security but before that I investigate first if these websites are trusted and safe. Then I go to www.scamadviser.com, I check the trust rating of these websites, luckily they got a high trust rating. Therefore these websites are advisable to be a “Password Checker”. (See the list of websites below which offers a free service in checking a password security.)
A Microsoft Password Checker, checks your password strength and rate it in four categories: weak, medium, strong and best. It offers also some tips about how to create passwords that are easy for you to remember but difficult for others to guess.
Author: Jexter B.
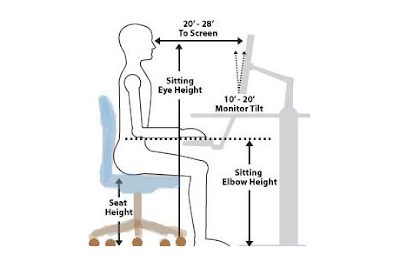
Right Body Posture in Front of Computer
At this point, a lot of us spend our day facing a PC, typing away, sitting uncomfortably, and chatting on the handset without using our hands to be able to finalize our job. The majority of us also suffer pain from neck, back as well as eye anxiety. Did you realize that is a right method to sit down at the computer desk which can help you ease the pain as well as discomfort.
So what is correct computer posture? Several body placements that work together to ensure you suffer the least amount of strain, including the best position to of your eyes, back, neck, foot and knee placements. Even lighting can have a strong impact on our bodies.
Bad computer posture symptoms can be sore wrists, shoulder and neck strain as well as low back pain, tired eyes and even headaches. Long term bad posture can cause long term chronic pain, but can easily resolved by taking the time to ensure we are sitting correctly.
Many offices now work to improve their employee’s computer posture to ensure their long term health and happiness. Taking these relatively few measures of safety is more than just a luxury and could raise your productivity at work thus the potential benefits of these measures by far outweigh the costs if any.
Have a look at the above diagram, and check in with your body. After a long day of sitting at your desk, where does your body feel strain, there is probably a change that needs to be made. Talk to your employer about getting an ergonomics specialist to come in and check out the workstations of all their employees. If you are suffering from strain, make an appointment to assist you in finding some relief.
Via: backtowellness.ca
Top 10 Improvements on Car Engines
Most of us know that the Ford Model T was the first truly affordable automobile. But do you know what kind of engine it had? The original Model T, released in 1908, packed a 2.9-liter four-cylinder engine with just 22 horsepower.
That's a tiny output for its size compared to the engines of today, but it sure beat the engine in what's considered to be the first automobile -- the 1885 Benz Patent Motorwagen. That car had a single-piston engine and generated just two-thirds of a single horsepower.
As you can see, automobile engines have been in constant evolution since the very beginning of motoring. Today they are more powerful, quieter, more durable, less polluting and more fuel-efficient than they have ever been before, thanks to constant advancements in engine design and technology.
Automotive engineers are constantly working on ways to improve the internal combustion engine and carry it into the future. How many other inventions do you know that have been continuously refined for more 150 years?
In this article, we'll take a look at 10 of the biggest and most significant engine improvements of all time. From fuel injection to hybrid motors, we'll take a look at where engines have been, and hopefully get some insight on where they're headed.
1. The Four-stroke Engine Cycle

Historic car enthusiast Ian Sumner checks the engine of a Jaguar D-Type replica classic car which is displayed at the annual RNAS Yeovilton Air Day in Yeovil, England.
Benefits: More fuel-efficient, less polluting
Drawbacks: More complicated, more expensive to manufacture
Remember that Benz Patent Motorwagen we talked about? In addition to having a single piston, or cylinder, it was a two-stroke engine, like many early motors. Stroke refers to the movement of the piston in the engine.
Four-stroke engines were one of the earliest improvements made to internal combustion engines in the late 1800s. On a four-stroke engine, there are four steps the engine takes as it burns gasoline: intake, compression, power, and exhaust [via: CompGoParts.com]. These steps all occur when as piston moves up and down two times.
Earlier, simpler two-stroke engines accomplish the same task -- burning gasoline to create mechanical motion -- but they do it in two steps. Today, two-stroke engines are found on small equipment like lawnmowers, small motorcycles, and large, industrial engines. Nearly all cars use the four-stroke cycle.
Four-stroke engines carry several benefits, including improved fuel economy, more durability, more power and torque, and cleaner emissions. However, compared to two-stroke engines, they are more complicated and expensive to make, and require the use of valves for the intake and exhaust of gases.
In spite of this, four-stroke engines have become the industry standard for cars, and they likely aren't going away any time soon. We'll learn more about the role of valves and how they've been improved upon later in this article.
Next, we'll learn about forced induction, and how it made its way from airplanes onto everyday cars.
2. Forced Induction

Turbochargers and superchargers are essentially air compressors that shove more air into the engine.
Benefits: More power without an increase in engine size
Drawbacks: Fuel consumption, turbo lag
An engine requires three things to generate motion: fuel, air, and ignition. Cramming more air into an engine will increase the power generated by the engine's pistons. A long-standing way to do that, and one that's becoming increasingly popular as of late, is to use forced induction. You may know this process better by the parts that do make it happen --turbochargers and superchargers.
In a forced induction engine, air is forced into the combustion chamber at a higher pressure than usual, creating a higher compression and more power from each stroke of the engine [via: Bowman]. Turbochargers and superchargers are essentially air compressors that shove more air into the engine.
Forced induction systems were used on aircraft engines long before they started being added to car engines in the 1960s. They are especially beneficial for small engines as they can generate a lot of extra power without increasing the engine's size or causing a dramatic drop in fuel economy.
A good example is the turbocharged Mini Cooper S, which only has a 1.6-liter engine but produces more than 200 horsepower in some applications. In addition, high-performance cars like the Porsche 911 Turbo or Corvette ZR-1 use forced induction to achieve tremendous gains in power.
The drawbacks? Cars that have turbochargers often require premium gasoline. Then there's the issue ofturbo lag, where the power gains aren't felt until the turbocharger spools up at higher revolutions per minute (RPM). Engineers have helped reduce both of those drawbacks in recent years.
And with fuel economy and emissions standards getting stricter, many carmakers are turning to forced induction on smaller engines instead of building larger engines. On the newest Hyundai Sonata, for example, the top engine one can buy is no longer a V6, but a turbo four-cylinder.
Next up, we'll discuss why carburetors have practically become a thing of the past thanks to fuel injection.
3. Fuel Injection

Why did fuel injection replace the carburetor?
Benefits: Better throttle response, increased fuel efficiency, more power, easier starting
Drawbacks: More complexity and potentially expensive repairs
For decades, the preferred method for mixing fuel and air and depositing it into the engine's combustion chamber was thecarburetor. Press the accelerator pedal to full throttle, and the carburetor allows more air and fuel into the engine.
Since the late 1980s, carburetors have been almost completely replaced by fuel injection, a far more sophisticated and effective system of mixing fuel and air. Fuel injectors spray gasoline into the air intake manifold, where fuel and air mix together into a fine mist. That mix is brought into the combustion chamber by valves on each cylinder during the intake process. The engine's on-board computer controls the fuel injection process.
So why did fuel injection replace the carburetor? To put it simply, fuel injection just works better in every aspect. Computer-controlled fuel-injected engines are easier to start, especially on cold days, when carburetors could make things tricky. Engines with fuel injection are also more efficient and more responsive to changes in the throttle [via: Automedia].
They do have drawbacks in terms of their increased complexity. Fuel injection systems are more costly to repair than carburetors as well. However, they have become the industry standard for fuel delivery, and it doesn't look like carburetors will be making a comeback anytime soon.
In this next section, we'll discuss the next step in fuel injection technology known as direct injection.
4. Direct Injection

One of the benefits of direct injection is better fuel economy.
Benefits: More power, better fuel economy
Drawbacks: More expensive to make, relatively new technology
Direct injection is a further refinement of the improvements made by fuel injection. As you may have guessed from its name, it allows fuel injection to "skip a step," which adds efficiency to the engine, and more power and improved fuel economy as a consequence.
On a direct injection engine, fuel is sprayed directly into the combustion chamber, not into the air intake manifold. Engine computers then make sure the fuel is burned exactly when and where it is needed, reducing waste. Direct injection provides a leaner mix of fuel, which burns more efficiently. In some ways it makes gasoline-powered engines more similar to diesel engines, which have always used a form of direct injection.
As we learned earlier, direct injection engines boast an increase in power and fuel economy over stand fuel injection systems. But they have their drawbacks as well. For one, the technology is a relatively new one, having come to market only in the last decade or so. More and more companies are starting to increase their use of direct injection, but it has yet to become the standard.
Sometimes, direct injection engines can exhibit the buildup of carbon deposits on the intake valves, which could cause reliability issues. Some car tuners have expressed difficulty with modifying direct injection engines as well. Despite these issues, direct injection is the hot new technology in the automotive world right now. Expect to see it on more and more cars as time goes on.
Next, let's look at the use of aluminum engine blocks vs. old-school iron blocks.
5. Aluminum engine blocks

For many years, iron engine blocks were the industry standard -- now the majority of new small engines use aluminum instead.
Benefits: Lighter weight leads to more efficiency and better handling
Drawbacks: Can warp at high temperatures
Over the past few years, cars have been trending towards being more lightweight in many ways. Automakers look for ways to reduce a vehicle's weight in order to generate betterfuel economy and performance. One of the ways they've done that is largely by replacing engines made of iron with aluminum ones.
For many years, iron engine blocks were the industry standard. Today the majority of all new small engines use aluminum instead, though many large V8 engines still use iron blocks. Aluminum weighs far less than iron -- typically, an aluminum engine weighs half what an iron one weighs. That translates into an overall lighter weight for the car, which means better handling and more fuel efficiency [via: Murphy].
Aluminum does have some drawbacks, however. As a metal, it's not as strong as iron and doesn't hold up to high levels of heat as well. Many early aluminum block engines had problems with cylinders warping, leading to concerns over durability. Those problems have been largely solved, however, and aluminum has clearly asserted itself as the future of engines due to its weight-saving properties.
In this next section, we'll talk about how camshafts have revolutionized engine design.
6. Overhead Camshafts

The benefit to the overhead cam setup is that it allows for more intake and exhaust valves, meaning fuel, air and exhaust can move more freely through the engine, adding power.
Benefits: Better performance
Drawbacks: Increased complexity
You've probably heard the term "DOHC" or "dual overhead camshafts" when someone talks about an engine. Most people recognize it as a desirable feature to have, but what does it mean? The term refers to the number of overhead camshafts above each cylinder in the engine.
Camshafts are part of your car's valvetrain, which is a system that controls the flow of fuel and air into the cylinders. For many decades cars primarily had OHV engines, meaning overhead valves, also called "pushrods." Pushrods are driven by camshafts inside the engine block. This setup adds mass to the engine and can limit its overall speed.
On an overhead cam setup, the camshaft is much smaller and is inserted above the cylinder head itself, rather than in the engine block. There's one on a single overhead cam SOHC engine, while a DOHC engine has two. The benefit to the overhead cam setup is that it allows for more intake and exhaust valves, meaning fuel, air and exhaust can move more freely through the engine, adding power.
While many car companies have done away with pushrod engines, DOHC and SOHC haven't supplanted them quite yet. Chrysler still uses pushrods to generate lots of power for their Hemi V8 engines; General Motors utilizes pushrods on some of their high-tech, modern V8s as well. But DOHC and SOHC engines have been prominent on engines, especially smaller ones, since the 1980s.
The drawback of having overhead cams is that they increase complexity and cost. Are you noticing a trend here yet?
Next we'll learn more still about how valves affect performance when we talk about variable valve timing.
7. Variable Valve Timing

People who tune their Hondas for performance often speak of "VTEC kicking in." But what exactly does that mean?
Benefits: Fuel economy, more flexible power delivery
Drawbacks: Greater cost to produce
If you're at all familiar with Honda engines, you've almost certainly heard the term VTEC. People who tune their Hondas for performance often speak of "VTEC kicking in." But what exactly does that mean?
VTEC refers to variable valve timing and lift electronic control, a form of variable valve timing. There are times when an engine requires more air flow, like during hard acceleration, but a traditional engine often does not allow enough air to flow, resulting in lower performance. Variable valve timing means the flow of air in and out of the valves is slowed down or sped up as needed [via: Autropolis].
Honda is hardly the only car company to offer such a system. Toyota has one they call VVT-i, for variable valve timing with intelligence, and BMW has a system called Valvetronic or VANOS, which stands for variable Nockenwellensteuerung, meaning variable camshaft control. While they all work a little differently, they all accomplish the same task -- allowing more air and fuel into the valves at different speeds. This makes an engine more flexible and allows it to deliver peak performance in a variety of conditions. It also increases fuel economy.
Many engines now incorporate some form of variable valve timing, often controlled by the engine's on-board computer. We'll talk about how engine computers have revolutionized design in this next section.
8. On-board Engine Computers

Modern cars have everything regulated by an on-board computer called an engine control unit, or ECU.
Benefits: Fuel economy, better diagnosis of problems
Drawbacks: Cost, complexity
An engine is an incredibly sophisticated device. It has dozens of moving parts and has scores of different processes taking place at once. That's why modern cars have everything regulated by an on-board computer called an engine control unit, or ECU.
The ECU makes sure processes like ignition timing, the air/fuel mixture, fuel injection, idle speed, and others operate the way they're supposed to. It monitors what's going on in the engine using an array of sensors and performs millions of calculations each second in order to keep everything operating correctly. Other computers in the car control things like electrical systems, airbags, interior temperature, traction control, anti-lock brakes and the automatic transmission.
Cars have become increasingly computerized since the first on-board diagnostic OBD computers were added in the 1980s. That's the computer that's responsible for the "check engine" light on your dashboard. A mechanic can plug a computer into the OBD port and get a sense of your car's problem areas. They can't use OBD to immediately know what's wrong with your car, but it gives them a great starting point.
By making the engine run more efficiently, engine computers can result in greater fuel efficiency and easier diagnosis of problems. But they also make engines far more complicated, and can make them tricky for weekend mechanics to work on.
Next up: Let's learn why diesel engines aren't the smoky, noisy, low-power oil burners of the past.
9. Clean Diesels

An Audi Q7 TDI clean diesel on display at Grand Central Station in New York City.
Benefits: Torque, fuel economy, cleaner emissions
Drawbacks: Cost of fuel, low RPMs, higher initial cost
We've talked a lot about gasoline engines so far, but what about diesel engines? Diesels have never been big sellers in the United States. Despite their superior fuel economy over similar gas engines, many Americans still think of diesels as the noisy, sooty, smelly, unreliable motors of the 1970s and 1980s.
That's not the case anymore. The modern diesel engine is powerful, clean and extremely fuel-efficient. Today's engines use a low-sulfur form of diesel fuel, and systems within the car help eliminate particle matter and excess pollution.
The diesels made by companies like Volkswagen, Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Volvo and others boast engine improvements like turbocharging, sophisticated fuel injection, and computer control to provide a driving experience that's both efficient and high in torque [via: Bosch].
Diesel engines have some drawbacks, mainly their low RPM level and the higher cost of diesel fuel. But since many of them can achieve well over 40 miles per gallon (17 kilometers per liter) on the highway, the driver will need to pay for that fuel a lot less often. And if you're wondering if modern diesels offer good performance, look no further than the last few 24 Hours of Le Mans races, where Audi has dominated using a diesel racecar.
Finally, we'll look at the current leader in "green" cars the hybrid engine.
10. Hybrid Engines

One of the biggest engine improvements used to boost efficiency in recent years is the hybrid engine.
Drawbacks: Higher initial cost, complexity
A combination of high gas prices, an increased awareness of the environment among drivers, and government regulations raising fuel economy and emissions standards have forced engines to "go green" more than ever before. One of the biggest engine improvements used to boost efficiency in recent years is the hybrid engine.
Hybrids were an obscure a decade ago, but now everyone knows how they work -- an electric motor is partnered with a traditional gasoline engine in order to achieve high fuel economy numbers, but without the "range anxiety" of an electric engine, where the driver always wonders what will happen when a charge runs out.
The Toyota Prius remains the top selling hybrid car in America. It boasts a 1.8-liter four cylinder engine coupled with an electric motor that produces 134 horsepower. At low speeds, the electric engine acts alone, meaning the car does not use gas at all. At other times, it assists the gasoline engine. The whole package gets about 50 miles per gallon (21.3 kilometers per liter) in both the city and the highway [via: AOL Autos].
Hybrids like the Prius represent the latest evolution in internal combustion technology. While their benefits come in the form of fuel efficiency, there are some drawbacks as well. Hybrids have a higher initial cost than their non-hybrid counterparts, and some have argued that gas must be much more expensive than it is now (unbelievable as that may sound) before the driver recoups the extra cost of the hybrid car.
Via: howstuffworks.com
Via: howstuffworks.com